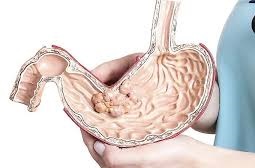
Gastric cancer is a malignant tumor originating from the epithelium of the gastric mucosa.
Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancers. About 1 million new cases are detected annually in the world. In the structure of oncological morbidity in Kazakhstan, stomach cancer ranks 3rd and 2nd in terms of mortality. About 2,700 new cases of stomach cancer are detected annually in Kazakhstan, that is, 14.4 per 100,000 population, and the death rate from this disease is 1,700 cases, or 9.1 per 100,000 population. Most stomach cancer occurs in men. It can develop anywhere in the stomach and spread to other organs, especially the esophagus, lungs, and liver.
Causes and factors for the development of stomach cancer:
The causes of stomach cancer, as well as cancer in general, are not fully understood. There are a number of factors that predispose to the development of stomach cancer. These include:
heredity. The presence of close relatives with a history of stomach cancer;
polyps of the stomach or adenomatous polyposis;
peptic ulcer and chronic gastritis;
elevated levels of Helicobacter pylori;
duodenogastric reflux;
intestinal metaplasia - replacement of the gastric epithelium with intestinal;
malnutrition - a large amount of salty, spicy and smoked foods, animal fats, low content of vegetables and fruits;
the use of low-quality and expired products;
lack of vitamins and minerals;
smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
age over 60 years, especially in men;
5-10 years after gastric surgery.
Symptoms:
Gastric cancer is always preceded by a "precancerous condition", i.e. certain changes in the cells lining the stomach - metaplasia and dysplasia of the epithelium of the stomach. Such changes can occur in chronic atrophic gastritis. Gastric cancer at an early stage shows general and nonspecific symptoms.
The so-called “small signs” syndrome can be observed: asthenia, aversion to meat food, anemia, weight loss, gastric discomfort (more often with common forms of the process).
The reason for visiting a doctor and examination should be:
discomfort and pain in the epigastrium (the area above the navel) combined with nausea and loss of appetite;
difficulty swallowing (may occur due to involvement of the upper part of the stomach in the tumor);
feeling full when taking a small amount of food;
fatigue, weight loss;
Iron-deficiency anemia;
vomiting of blood or contents resembling "coffee grounds", black tarry stools (melena). Melena is a black semi-liquid stool with a characteristic unpleasant odor, formed from the blood under the influence of the contents of the stomach and intestines. The appearance of melena is an important signal for contacting an oncologist.
Diagnostic methods for suspected stomach cancer:
Endoscopic examination of the stomach. Using a thin flexible tube with a light, the doctor can examine the entire gastrointestinal tract. If a suspicious area is found in it, a biopsy is taken from it in order to make a microscopic examination.
Contrast study of the gastrointestinal tract. For this procedure, the sick person needs to use a little barium, which helps to cover the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, then several x-rays are taken. After receiving the result of the examination, air is introduced into the stomach through a small tube so that the barium is distributed over the mucous organ in an even layer. Using this method, you can get accurate data and determine the minimum changes in the gastric walls.
Computed tomography (CT). This technique uses a specialized x-ray technique, which makes it possible to take pictures from different angles. In this case, you can get detailed data on the tissues and organs of the gastrointestinal tract. After the examination, you can find out the prevalence of education, as well as determine which organs are already affected by metastases. It is with the help of this technique that a targeted biopsy of a suspicious area is carried out with its further study.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using this technique, like CT, the body is examined in layers. The peculiarity lies in the fact that a special magnet is used instead of radiation.
Positron emission tomography (PET). To carry out this method, it is necessary to inject radioactive glucose into the vein of a cancer patient, which is capable of concentrating in a malignant neoplasm, and using a scanner device, it is possible to detect a zone of its accumulation. The method allows you to determine the spread of the neoplasm, as well as find out at what stage the disease occurs.
Doctor's recommendations for the prevention of stomach cancer:
The main prevention of stomach cancer is to follow the diet: reduce the consumption of smoked and deep-fried foods, canned food, animal fats; refusal to abuse alcohol and smoking; saturate the diet with fruits and vegetables.
An important point in the prevention of stomach cancer is the treatment of precancerous conditions (polyposis of the stomach, chronic atrophic gastritis).
If you have any suspicions or want to be examined, please contact our clinic at the Call Center number 8(7172)702-911. At the NROC you can get qualified advice from an oncologist, the full range of diagnostic services and the definition of treatment tactics.