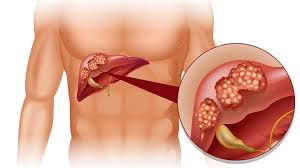
Liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma is a malignant tumor that is localized in the liver. More than 600,000 newly diagnosed cases are registered annually in the world. In Kazakhstan, more than 1,000 cases of illness are detected annually among the population, and the death rate is about 700 cases per year. The neoplasm originates from liver cells or may be a metastasis of another (primary) tumor.
Metastases in the liver develop much more often than primary tumors. This is due to the nature of blood circulation and liver function in the body. Metastasis of a malignant neoplasm is a severe complication that is more dangerous than the primary tumor itself. Metastatic cancer is detected as metastases of a malignant tumor in its primary localization in other organs.
Causes and factors for the development of liver cancer:
The causes and mechanism of the development of the disease are still not well understood. The influence of geographical location, climate, diet, and some medications was studied. In patients with alcoholism, primary hepatocellular carcinoma often develops against the background of cirrhosis. Liver cancer can be detected at any age, more often they get sick after 40 years.
Risk factors:
Liver diseases. Long-term infection with hepatitis B or C can seriously damage your liver.
Alcohol abuse. Drinking two or more alcoholic drinks every day for many years increases the risk of liver cancer.
Cirrhosis. A disease that develops as a result of the formation of scar tissue in the liver and often leads to cancer. The most significant causes of cirrhosis are alcohol consumption and hepatitis B and C. Another cause is the accumulation of excess iron in the liver.
Aflatoxins. Eating foods that, due to improper storage, are affected by aflatoxin B1 (mitotoxin of the fungus Aspergillus flavus), increases the risk of the disease. These products include: wheat, rice, corn, soybeans, peanuts, etc.
Diabetes and obesity. People with diabetes tend to be overweight or obese, which can cause liver problems and increase the risk of liver cancer.
Anabolic steroids are male hormones sometimes used by athletes. Their long-term use may slightly increase the risk of developing a malignant liver tumor.
Arsenic. There are countries where drinking water is contaminated with arsenic, which increases the risk of liver cancer.
Liver cancer symptoms:
Signs of liver cancer are nonspecific and can easily be confused with other diseases of this organ (with cholelithiasis or exacerbation of chronic hepatitis). Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time to make an accurate diagnosis and prevent the development of the disease if you notice the following symptoms:
constant bloating and discomfort;
frequent diarrhea or constipation;
nausea, which may be accompanied by vomiting (this is one of the most common symptoms of liver cancer);
loss of appetite;
constant feeling of fatigue and even malaise;
chills and fever, a feeling of a cold.
Diagnosis of liver cancer:
Diagnosis begins with the collection of anamnesis and physical examination. It is very important to tell your doctor if you have a history of long-term alcohol abuse or chronic hepatitis B or C infection.
Diagnostic tests and procedures for liver cancer include the following:
Liver function tests help your doctor determine the condition of your liver by measuring the levels of proteins, liver enzymes, and bilirubin in your blood.
The presence of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood may be a sign of liver cancer. This protein is normally only produced in the liver and yolk sac of babies before they are born. AFP production usually ceases after birth.
Abdominal CT or MRI, which provides detailed images of the liver and other abdominal organs. They can allow your doctor to pinpoint where the tumor is developing, determine its size, and assess whether it has spread to other organs.
Another available diagnostic test is a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy involves removing a small piece of liver tissue. This is always done under anesthesia so that you don't feel any pain during the procedure. In most cases, a needle biopsy is performed. During this procedure, your doctor will insert a thin needle through your abdomen and into your liver to obtain a tissue sample. The sample is then examined for signs of cancer.
Doctor's advice on how to prevent liver cancer:
The main measures to prevent liver cancer are:
timely vaccination against hepatitis B;
timely and high-quality treatment of hepatitis B and C;
treatment of alcoholism and complete rejection of alcohol;
regular monitoring by a hepatologist for patients with cirrhosis and chronic viral hepatitis (at least 2-3 times a year).
Of particular importance is the fight against alcoholism, since cirrhosis of the liver (especially large-nodular form) is found in approximately 60-90% of patients with liver hepatoma.
If you have any questions or want to be examined and find out about your health, you can contact our center by calling the Call Center 8(7172)702-911.